Introduction
Antibiotics refer to a class of secondary metabolites with anti-pathogen or other activities produced by microorganisms (including bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes) or higher animals and plants in the process of life.
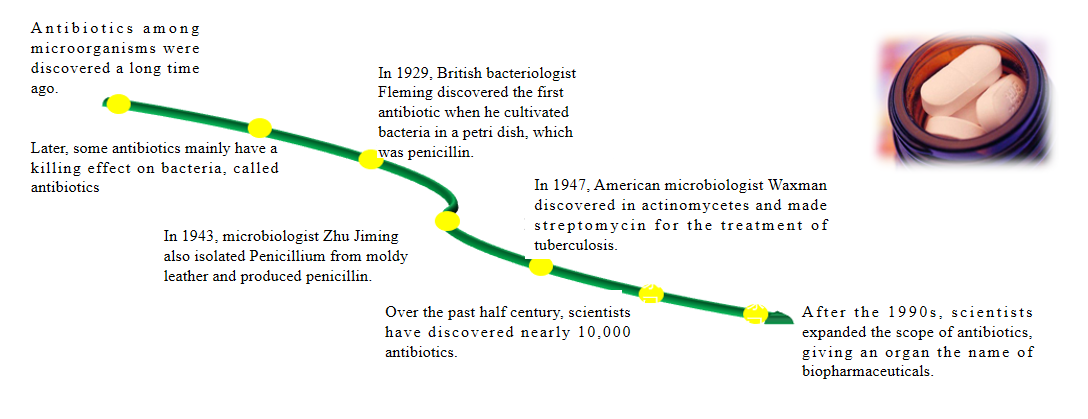
Fig 1. Discovery and development of antibiotics
Mechanism
The bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect of antibiotics is mainly aimed at killing the mechanism that "bacteria have but humans (or other animals and plants) do not".
Application
1) Screening of stably transfected cell lines
The most common application of antibiotics in molecular biology experiments is to screen and maintain cultured prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells carrying resistance genes.
|
Screening of stably transfected cell lines |
|
|
Screen for antibiotics |
Most Common Screening Uses |
|
Eukaryotes and Bacteria |
|
|
Blasticidin S (inquire) |
Eukaryotes and Bacteria |
|
eukaryotes |
|
|
Dual Screening Experiments and Eukaryotes |
|
|
Aureobasidin A (AbA) (inquire) |
yeast |
2) Cell culture
Cell contamination is almost an inevitable problem encountered in the process of cell culture. Bacteria and fungi are extremely common pollutants in cell culture experiments. Antibiotics can be used in cell culture experiments to prevent or treat cell contamination by fungi and bacteria.
|
Commonly used antibiotics for cell culture |
|
|
Commonly used antibiotics for cell culture |
Types of Pollutants Controlled |
|
Penicillin |
Gram-positive bacteria |
|
Streptomycin |
Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria |
|
Gentamicin |
Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, Mycoplasma |
|
Amphotericin B |
Gram-positive bacteria, yeast, fungi |
|
Nystatin |
Yeasts, fungi |
3) Plant protectant
Fungi and bacteria can cause a variety of plant diseases. Another broad application of antibiotics is as plant protection agents. At a certain dose concentration, it is used alone or in combination to protect plants from the harm of pathogenic infection.
4) Animal intestinal flora research
Animal gastrointestinal microbes can participate in a variety of host metabolic processes and play a crucial role in maintaining the body's healthy homeostasis. Specific types of antibiotics can interfere or regulate the number, types and activities of animal intestinal flora, so as to study the impact of changes in intestinal microorganisms on certain metabolic processes.
Product usage advice
Antibiotics are physiologically active substances, and various antibiotics usually act on pathogenic bacteria at very low concentrations, but the specific working concentration needs to be changed according to cell type, medium, growth conditions, cell metabolic rate and experimental purpose. Therefore, it is recommended to establish a kill curve, that is, a dose-response curve, to determine the optimal screening concentration for the experimental system used for the first time.
|
antibiotic name |
Preparation method |
Storage Concentration (mg/mL) |
Storage Conditions |
Reference working concentration (μg/mL) |
|
Ampicillin sodium salt |
Soluble in sterile water |
100 |
-20°C dispense |
50-100 |
|
Carbenicillin disodium salt |
Soluble in sterile water |
50 |
-20°C dispense |
0.1-30 |
|
kanamycin sulfate |
Soluble in sterile water |
10 |
-20°C dispense |
30-100 |
|
Chloramphenicol |
Soluble in absolute ethanol |
50 |
-20°C dispense |
5-20 |
|
streptomycin sulfate |
Soluble in sterile water |
50 |
-20°C dispense |
10-50 |
|
Tetracycline hydrochloride |
Soluble in sterile water |
5-10 |
-20°C, aliquoted and protected from light |
5-10 |
|
Puromycin hydrochloride |
Soluble in sterile water or methanol |
50 (sterile water) |
-20℃ dry |
Mammalian cells: 1-10 |
|
Rifampicin |
Soluble in DMSO |
50 |
-20°C, aliquoted and protected from light |
10-50 |
|
Timentin |
Soluble in sterile water |
200 |
-20°C dispense |
200 |
|
G418 Geneticin |
Soluble in sterile water |
/ |
-20°C, aliquoted and protected from light |
Mammalian cells: 200-2000 |
|
Hygromycin B |
Dissolved in 1x PBS (PH 7.4) |
50 |
-20°C dispense |
Mammalian cells: 50-500 |
Yeasen product performance
At present, the quality of antibiotic products on the market is uneven, and Yeasen is dedicated to provide you with a complete range of antibiotic products.
(1) High-quality raw materials, all antibiotic product raw materials are sourced from high-quality fixed suppliers;
(2) Standardized production, using factory mass production mode;
(3) Wide range of applications, which can be used in the fields of molecular biology and biochemical experimental research of tissue culture;
(4) The cooperation platform covers the whole;
(5) To ensure product quality stability, the difference between batches is controlled within 1%, as shown in Figure 3:
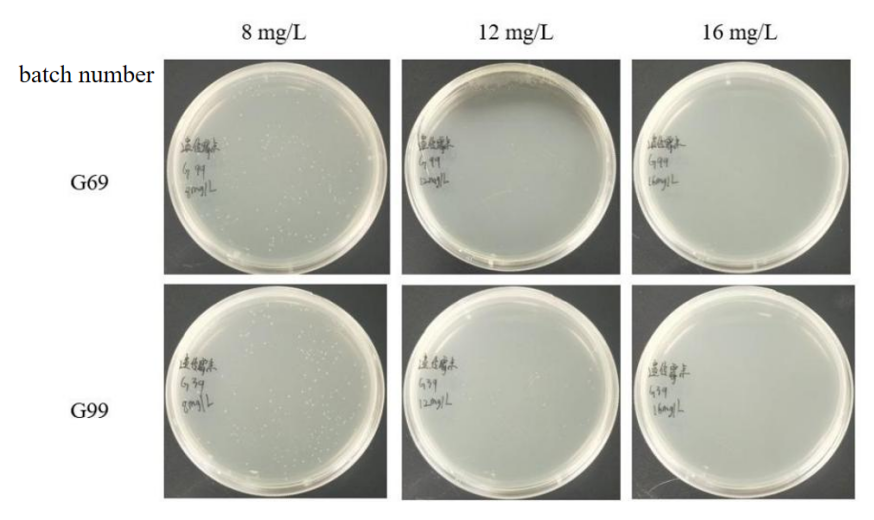
Fig 2. Stability test and effective concentration confirmation between different batches of Geneticin
【Note】G69 and G99 are different batches; the concentration of Geneticin is 8 mg/L, 12 mg/L, and 16 mg/L in turn, and the lowest effective concentration is determined to be 16 mg/L, which can perfectly inhibit miscellaneous bacteria. growth, the performance of the two batches was consistent.
Customer case
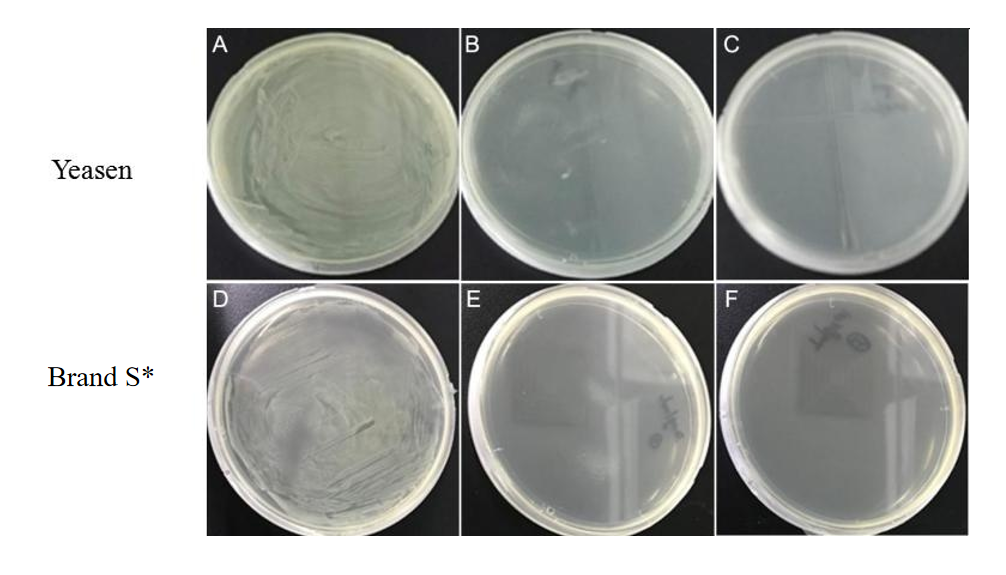
Fig 3. Colony growth of E. coli on hygromycin-resistant plates with different concentrations, Yeasen and brand S* have the same effect.
【Note】A-C are brand S* hygromycin 20 μg/ml, 50 μg/ml, 100 μg/ml plates, D-F are Yeasen hygromycin 20 μg/ml, 50 μg/ml, 100 μg/ml plates.
Ordering products
1. Antibiotics for Screening of Stably Transduced Cell Lines
|
Product name |
Cat# |
Size |
|
Puromycin Dihydrochloride (Inquire) |
60210ES25/60/72/76/80 |
25 /100 /250/500mg/1g |
|
60209ES60/76/77 |
10×1/50×1/1×50 mL |
|
|
Blasticidin S (10mg/ml in Solution) (Inquire) |
60218ES10/50 |
10/5×10 mg |
|
60220ES03/08 |
1/5 g |
|
|
Hygromycin B (50 mg/ml) (inquire) |
60224ES03 |
1 g (20 ml) |
|
60225ES03/10 |
1/10 g |
|
|
Aureobasidin A(AbA) (inquire) |
60231ES03/08 |
1/5×1 mg |
2. Commonly used antibiotics
|
Product name |
Cat# |
Size |
|
Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (Inquire) |
60201ES25/60 |
5/25/100 g |
|
Carbenicillin, Disodium Salt (Inquire) |
60202ES08/25 |
5/25/100 g |
|
60203ES10/60 |
10/100 g |
|
|
Doxycycline hyclate (Inquire) |
60204ES03/08 |
1/5 g |
|
60205ES08/25 |
5/25 g |
|
|
60206ES10/60 |
10/100 g |
|
|
60207ES25/60 |
25/100 g |
|
|
Penicillin G, Sodium Salt (Inquire) |
60208ES25/60 |
25/100 g |
|
Streptomycin Sulfate (Inquire) |
60211ES25/60 |
25/100 g |
|
60212ES25/60 |
25/100 g |
|
|
Vancomycin Hydrochloride (Inquire) |
60213ES60/80 |
100 mg/1 g |
|
Gentamycin Sulfate Salt (Inquire) |
60214ES03/08 |
1/5 g |
|
Spectinomycin Hydrochloride (Inquire) |
60215ES08 |
5 g |
|
Cefotaxime Sodium Salt (Inquire) |
60226ES03/08 |
1/5 g |
|
Rifampicin (Inquire) |
60234ES03/08 |
1/5 g |
|
Amphotericin B (Inquire) |
60238ES01/03 |
100 mg/1 g |
Published articles with our reagents
[1] Zhang S, et al. SNX10 (sorting nexin 10) inhibits colorectal cancer initiation and progression by controlling autophagic degradation of SRC. Autophagy. 2020 Apr;16(4):735-749. IF: 9.77
[2] Lu T, et al. CD73 in small extracellular vesicles derived from HNSCC defines tumour-associated immunosuppression mediated by macrophages in the microenvironment.J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 May;11(5):e12218. IF: 14.976
[3] Zhou YM, et al. BMP9 Reduces Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Mice by Dual Regulation of Bone Remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 2020 May;35(5):978-993. IF: 5.854
[4] Liu F, et al. CDK7 inhibition suppresses aberrant hedgehog pathway and overcomes resistance to smoothened antagonists.. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jun 25;116(26):12986-95. IF: 9.412
[5] Liu C, et al. A programmable hierarchical-responsive nanoCRISPR elicits robust activation of endogenous target to treat cancer. Theranostics. 2021 Oct 11;11(20):9833-9846. IF: 8.579
[6] Zhu G, Yu J, Sun Z, et al. Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screening identifies CARHSP1 responsible for radiation resistance in glioblastoma[J]. Cell death & disease, 2021, 12(8): 1-9. IF: 8.469
[7] Wang L, Wu W, Zhu X, et al. The ancient Chinese decoction Yu-Ping-Feng suppresses orthotopic Lewis lung cancer tumor growth through increasing M1 macrophage polarization and CD4+ T cell cytotoxicity[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2019, 10: 1333. IF: 5.810
[8] Huang H, Zou X, Zhong L, et al. CRISPR/dCas9‐mediated activation of multiple endogenous target genes directly converts human foreskin fibroblasts into Leydig‐like cells[J]. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 2019, 23(9): 6072-6084. IF: 5.310
[9] Wang Y, Jia M, Yan X, et al. Increased neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) promotes airway remodelling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Clinical Science, 2017, 131(11): 1147-1159.IF=6.124
[10] Su J, Sun H, Meng Q, et al. Enhanced Blood Suspensibility and Laser-Activated Tumor-specific Drug Release of Theranostic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Functionalizing with Erythrocyte Membranes[J]. Theranostics, 2017, 7(3): 523.IF=11.556
[11] Zhang T Q, Wang J W. Shoot Regenerative Capacity Assays in Arabidopsis and Tobacco[J].The Plant Cell, 2015.IF=11.277
[12] Yao C, Ni Z, Gong C, et al. Rocaglamide enhances NK cell-mediated killing of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting autophagy[J]. Autophagy, 2018, 14(10): 1831-1844.IF=16.016